Select Chapter Topics:
The EMF generated in a moving rod within a uniform magnetic field \(B\) is \(0.08~\text{V}.\) The speed \((v)\) of the rod is:

1.
\(1\) m/s
2.
\(2\) m/s
3.
\(3\) m/s
4.
\(4\) m/s
Subtopic: Motional emf |
92%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
In given L-R circuit connected with a D.C source of 12V, inductance is LmH and resistances is 6 Ω. If the emf induced in the inductor at t = 1mS is 10V, value of L is:

1. \({{3}\over{\ln\left({1.2}\right)}}\)
2. \({{6}\over{\ln\left({1.2}\right)}}\)
3. \({{3}\over{\ln\left({1.8}\right)}}\)
4. \({{6}\over{\ln\left({2.4}\right)}}\)

1. \({{3}\over{\ln\left({1.2}\right)}}\)
2. \({{6}\over{\ln\left({1.2}\right)}}\)
3. \({{3}\over{\ln\left({1.8}\right)}}\)
4. \({{6}\over{\ln\left({2.4}\right)}}\)
Subtopic: LR circuit |
62%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Consider the following Assertion and Reason:
| Assertion (A): | Moving magnet in conducting pipe slows down. |
| Reason (R): | Because eddy current is formed. |
| 1. | (A) is correct but (R) is wrong. |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are wrong. |
| 3. | Both (A) and (R) are correct. |
| 4. | (A) is wrong but (R) is correct. |
Subtopic: Eddy Current |
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
A cube with side length \(25~\text{cm}\) is moving with a uniform velocity of \(8~\text{m/s}\) in the positive \(y\)-direction, as shown in the figure. The cube is placed in a uniform magnetic field of \(1~\text{T},\) which is directed along the negative \(z\)-axis. The magnitude of the induced EMF across the opposite faces of the cube is:


| 1. | \(2~\text{V}\) | 2. | \(4~\text{V}\) |
| 3. | \(8~\text{V}\) | 4. | \(6~\text{V}\) |
Subtopic: Motional emf |
74%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Variation of the magnetic field through a coil of area \(4 ~\text m^2\) is shown in the figure. What is the emf induced in the coil (in mV)?
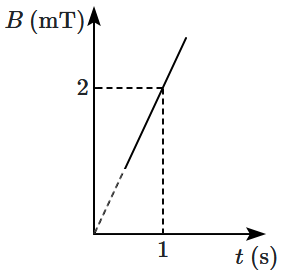
1. \(8 ~\text{mV}\)
2. \(16~\text{mV}\)
3. \(4 ~\text{mV}\)
4. \(2 ~\text{mV}\)

1. \(8 ~\text{mV}\)
2. \(16~\text{mV}\)
3. \(4 ~\text{mV}\)
4. \(2 ~\text{mV}\)
Subtopic: Faraday's Law & Lenz Law |
77%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
A circular ring is placed in a magnetic field of \(0.4\) T. Suddenly its radius starts shrinking at the rate of \(1\) mm/s. What will be the induced EMF in the ring at \(r = 2~\text{cm?}\)
1. \(16 \pi~\mu \text{V}\)
2. \(8 \pi~\mu \text{V}\)
3. \(16 \pi~ \text{mV}\)
4. \(8 \pi~ \text{mV}\)
1. \(16 \pi~\mu \text{V}\)
2. \(8 \pi~\mu \text{V}\)
3. \(16 \pi~ \text{mV}\)
4. \(8 \pi~ \text{mV}\)
Subtopic: Magnetic Flux |
66%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
A circular loop of radius \(\dfrac{10}{\sqrt{\pi}}\) cm is placed in a linearly varying perpendicular magnetic field which has magnitude \(0.5\) T at time \(t=0.\) The magnetic field reduces to zero at \(t=0.5~\text{s}\). The emf induced in the loop at \(t=0.25~\text{s}\) is:
(where \(r\) is the radius of the circular loop)

(where \(r\) is the radius of the circular loop)

| 1. | \(0.01~\text{V}\) | 2. | \(0.005~\text{V}\) |
| 3. | \(0.02~\text{V}\) | 4. | \(0.03~\text{V}\) |
Subtopic: Faraday's Law & Lenz Law |
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
In a part of the circuit, as shown, it is given that the current is decreasing at a rate of \(1~\text{A/s}.\) Then \(V_A-V_B\) is equal to:

1. \(18~\text{V}\)
2. \(-18~\text{V}\)
3. \(9~\text{V}\)
4. \(-9~\text{V}\)

1. \(18~\text{V}\)
2. \(-18~\text{V}\)
3. \(9~\text{V}\)
4. \(-9~\text{V}\)
Subtopic: LR circuit |
80%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
The magnetic field through a circular loop is \(0.8\) T. The radius of the loop is expanding at the rate of \(2\) cm/s. The induced emf in the loop, when the radius of the loop is \(10\) cm is:
1. \(32\times 10^{-4}\) V
2. \(16\times 10^{-4}\) V
3. \(32\times 10^{-2}\) V
4. \(16\times 10^{-2}\) V
1. \(32\times 10^{-4}\) V
2. \(16\times 10^{-4}\) V
3. \(32\times 10^{-2}\) V
4. \(16\times 10^{-2}\) V
Subtopic: Faraday's Law & Lenz Law |
74%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
A small circular loop of radius \(r\) is placed in the plane of a square loop of side length \(L\) \((r \ll L).\) A circular loop is at the center of the square as shown in the figure. The mutual inductance of the given system is:


| 1. | \({\dfrac{\mu_{0}r^{2}}{\sqrt{2}L}}\) | 2. | \({\dfrac{\pi\mu_{0}r^{2}}{2L}}\) |
| 3. | \({\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}\mu_{0}r^{2}}{L}}\) | 4. | \({\dfrac{4\mu_{0}r^{2}}{L}}\) |
Subtopic: Mutual Inductance |
67%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.




