Select Chapter Topics:
The equivalent resistance between points \(A\) and \(B\) in the given network is:

1. \(65~\Omega\)
2. \(20~\Omega\)
3. \(5~\Omega\)
4. \(2~\Omega\)
Subtopic: Combination of Resistors |
83%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
The current density in a cylindrical wire of radius \(4~\text{mm}\) is \(4 \times 10^6~ \text{Am}^{-2}\). The current through the outer portion of the wire between radial distance \(R \over 2\) and \(R\) is:
1. \(16\pi~\text{A}\)
2. \(64\pi~\text{A}\)
3. \(32\pi~\text{A}\)
4. \(48\pi~\text{A}\)
1. \(16\pi~\text{A}\)
2. \(64\pi~\text{A}\)
3. \(32\pi~\text{A}\)
4. \(48\pi~\text{A}\)
Subtopic: Current & Current Density |
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
The current density in a cylindrical wire of radius \(r= 4.0~\text{mm}\) is \(1.0 \times 10^6 ~\text{A/m}^2\). The current through the outer portion of the wire between radial distances \(\frac{r}{2}\) and \(r\) is \(x\pi~ \text{A}\), where \(x\) is:
1. \(10\)
2. \(14\)
3. \(16\)
4. \(12\)
1. \(10\)
2. \(14\)
3. \(16\)
4. \(12\)
Subtopic: Current & Current Density |
57%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
In the given circuit, \(a\) is an arbitrary constant. The value of \(m\) for which the equivalent circuit resistance is minimum will be \(\sqrt{\frac{x}{2}}.\) The value of \(x \) is:

1. \(6\)
2. \(9\)
3. \(3\)
4. \(12\)

1. \(6\)
2. \(9\)
3. \(3\)
4. \(12\)
Subtopic: Combination of Resistors |
68%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
A meter bridge setup is shown in the figure. It is used to determine an unknown resistance \(R\) using a given resistor of \(15~\Omega.\) The galvanometer \((G)\) shows a null deflection when the tapping key is at \(43~\text{cm}\) mark from end \(A\). If the end correction for end \(A\) is \(2~\text{cm}\), then the determined value of \(R\) will be:

1. \(19~\Omega\)
2. \( 22~\Omega\)
3. \(25~\Omega\)
4. \( 28~\Omega\)

1. \(19~\Omega\)
2. \( 22~\Omega\)
3. \(25~\Omega\)
4. \( 28~\Omega\)
Subtopic: Meter Bridge |
74%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Current measured by the ammeter \(A\) in the reported circuit when no current flows through \(10~\Omega\) resistance will be:

1. \(20~\text{A}\)
2. \(30~\text{A}\)
3. \(10~\text{A}\)
4. \(0~\text{A}\)

1. \(20~\text{A}\)
2. \(30~\text{A}\)
3. \(10~\text{A}\)
4. \(0~\text{A}\)
Subtopic: Wheatstone Bridge |
72%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Resistance of the wire is measured as \(2~\Omega\) and \(3~\Omega\) at \(10^{\circ}\text{C}\) and \(30^{\circ}\text{C}\) respectively. The temperature co-coefficient of resistance of the material of the wire is:
1. \(0.033^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1}\)
2. \(-0.033^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1}\)
3. \(0.011^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1}\)
4. \(0.055^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1}\)
1. \(0.033^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1}\)
2. \(-0.033^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1}\)
3. \(0.011^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1}\)
4. \(0.055^{\circ}\text{C}^{-1}\)
Subtopic: Heating Effects of Current |
80%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
All resistances in the figure are \(1~\Omega\) each. The value of the current \(I\) is \(\frac{a}{5}~\text{A}\). The value of \(a\) is:
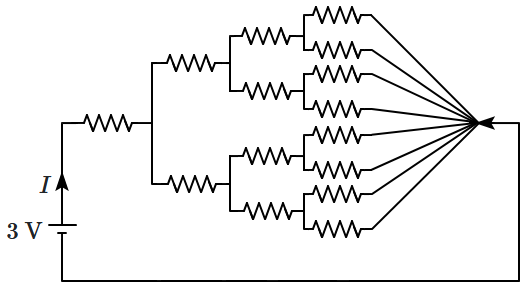
1. \(8\)
2. \(6\)
3. \(12\)
4. \(4\)

1. \(8\)
2. \(6\)
3. \(12\)
4. \(4\)
Subtopic: Combination of Resistors |
74%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
An aluminium wire is stretched to make its length, \(0.4\%\) larger. Then, the percentage change in resistance is:
1. \(0.4\%\)
2. \(0.2\%\)
3. \(0.8\%\)
4. \(0.6\%\)
1. \(0.4\%\)
2. \(0.2\%\)
3. \(0.8\%\)
4. \(0.6\%\)
Subtopic: Derivation of Ohm's Law |
86%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
The length of a given cylindrical wire is increased to double of its original length. The percentage increase in the resistance of the wire will be:
1. \(400\)
2. \(200\)
3. \(100\)
4. \(300\)
1. \(400\)
2. \(200\)
3. \(100\)
4. \(300\)
Subtopic: Derivation of Ohm's Law |
56%
From NCERT
JEE
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.






